Cryogenic Cable
Cryogenic Cable Features
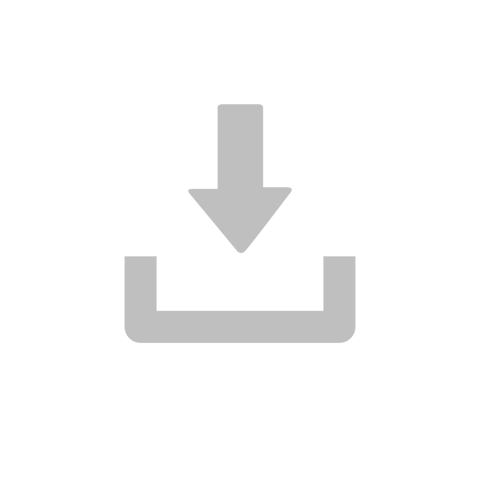
For high-frequency signals, Lake Shore provides various coaxial cables: ultra-miniature coaxial cables and semi-rigid coaxial with a stainless steel centre conductor.






Cables
Ultra miniature coaxial cable is for use when a strong and flexible cable is needed. Type SC is recommended when low conductor resistance is a prime consideration. Type SC and type SS are mechanically the most flexible, due to their braided construction. Type SS is recommended for use when both shielding and low thermal losses are important. For technical specifications on types SS, SC and SR, click here.
| Nominal attenuation (dB/m) | |||
| SC | SS | ||
| 1 MHz | 0.108 | 0.569 | |
| 5 MHz | 0.240 | 1.272 | |
| 10 MHz | 0.344 | 1.799 | |
| 15 MHz | 0.421 | 2.850 | |
| 20 MHz | 0.486 | 2.545 | |
| 50 MHz | 0.769 | 4.031 | |
| 100 MHz | 1.090 | 5.694 | |
| 500 MHz | 2.453 | 12.749 | |
| 1 GHz | 3.488 | 18.048 | |
| 2 GHz | — | — | |
| 5 GHz | 7.968 | 40.526 | |
Thermal conductivity of copper units are W/(m • K)
| 4 K | 20 K | 30 K | 77 K | 300 K | |
| RRR8 = 20 | 122 | 719 | 870 | 502 | 397 |
| RRR = 100 | 460 | 2460 | 2070 | 533 | 407 |
8 RRR = Residual Resistance Ratio
- Very flexible
- Long flex life
- Available in three configurations:
- SC — stranded copper conductors
- SS — stranded 304 stainless steel conductors
| Coaxial cable frequency response specifications | ||
| Frequency (GHz) | Insertion loss dB/m (dB/ft) | Power CW (20 °C, sea level, W) |
| 0.5 | 4.43 (1.35) | 7.6 |
| 1.0 | 6.27 (1.91) | 5.3 |
| 5.0 | 14.09 (4.30) | 2.4 |
| 10.0 | 20.01 (6.10) | 1.7 |
| 20.0 | 28.45 (8.67) | 1.2 |
This cable transmits and receives high-speed, high frequency microwave signals. Typically used for transmission lines in cryogenic-vacuum test systems.
To remove the outer conductor:
- Score jacket
- Bend at score until shield kinks, fatigues, and breaks
- Slide off outer conductor
Extreme caution must be used in this process to avoid damage to the coax
- Easily bent, coiled, stripped, machined, soldered, or connected without impairing performance
- Solid center conductor provides the optimum geometrical surface for transmission
- Low standing wave ratio (SWR) with a dielectric controlled to exacting tolerances
- Low thermal conductivity (≈0.4 W/(m · K) at 4.2 K)9
- Matching minimises reflective power loss
- Provides shielding isolation for virtually no extraneous signal pickup
- Tubular outer conductor offers minimum size and maximum conductor integrity; stainless steel jacket can be soldered directly to circuit boards
- 37 AWG, silver-plated copper-weld steel center conductor
9 Thermal conductivity at low temperatures is dominated by the copper cladding around the centre conductor
A robust, 4-wire cable for use in cryogenic environments to room temperature is now available. The cable is designed around 32 AWG (203 µm) diameter superconductive wires consisting of a NbTi core (128 µm diameter) and a Cu-10% Ni jacket.
The cable is constructed as follows:
- 4 superconductive wires are overcoated with 75 µm (0.003 in) thick Teflon® (PFA) of the following colours: white, yellow, green, and black.
- 4 lengths of Teflon®-jacketed wire, one of each colour, twisted together with a twist pitch of about 25 mm (1 in). Teflon® (PFA) is extruded over the 4 wires to a total diameter of about 1.2 mm (0.048 in).
- Cable is overbraided with 304 stainless steel (5 × 36 AWG). The overbraid is tight and presents complete visual coverage.
- Teflon® (PFA) extruded over the entire cable for protection of the metal overbraid. The total finished cable is nearly round with a diameter of about 2.4 ±0.2 mm (0.094 ±0.008 in).
Minimum bend radius: 15 mm (0.6 in)
Critical temperature: 9.8 K
Critical field: 10 T
| Field | Critical current (per wire) |
| 3 T | 35 A |
| 5 T | 25 A |
| 7 T | 15 A |
| 9 T | 6 A |
| Temperature (K) | |||
| 295 | 77 | 4.2 | |
| Wire resistance (Ω/m) | 9.2 | 8.4 | 010 |
| Overbraid resistance (Ω/m) | 0.90 | 0.64 | 0.62 |
| Thermal conductivity — entire cable assembly (W/(m•K)) | 7.6 | 2.8 | 0.17 |
10 Superconducting
- Robust: the NbTi wire cores are strong and fatigue resistant, and the cable overbraid of 304 stainless steel adds significant strength and crush resistant
- Low heat leak due to all metal alloy and Teflon® construction
- Solderable: the CuNi wire surface is easy to solder with conventional rosin fluxes
- Cryo-compatible: all Teflon® (PFA) insulation is heat strippable for ease of preparation