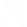Click here to discover more
Imaging Cameras
A Wide Range of Camera Solutions

Our Extensive Range
We have teamed up with the world leaders in each specialism to provide a extensive range of imaging cameras, including thermal imaging, SWIR, CCD and EMCCD and X-Ray Cameras. We welcome the opportunity to discuss your requirements in further details.
InfraTec offers solutions for every kind of thermographic measurement task. Discover the new generation of stationary and handheld infrared cameras with megapixel formats – VarioCAM® High Definition and ImageIR® 10300. A comprehensive range of non-contact temperature measurement devices for your needs.
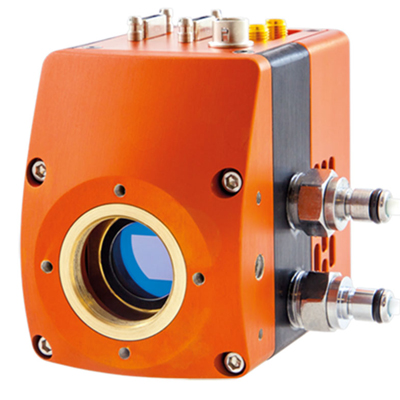
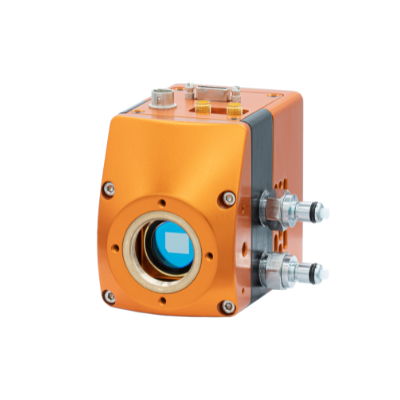
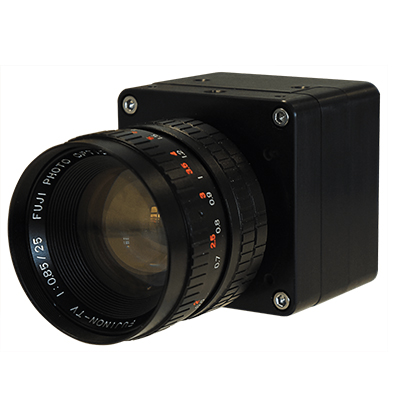
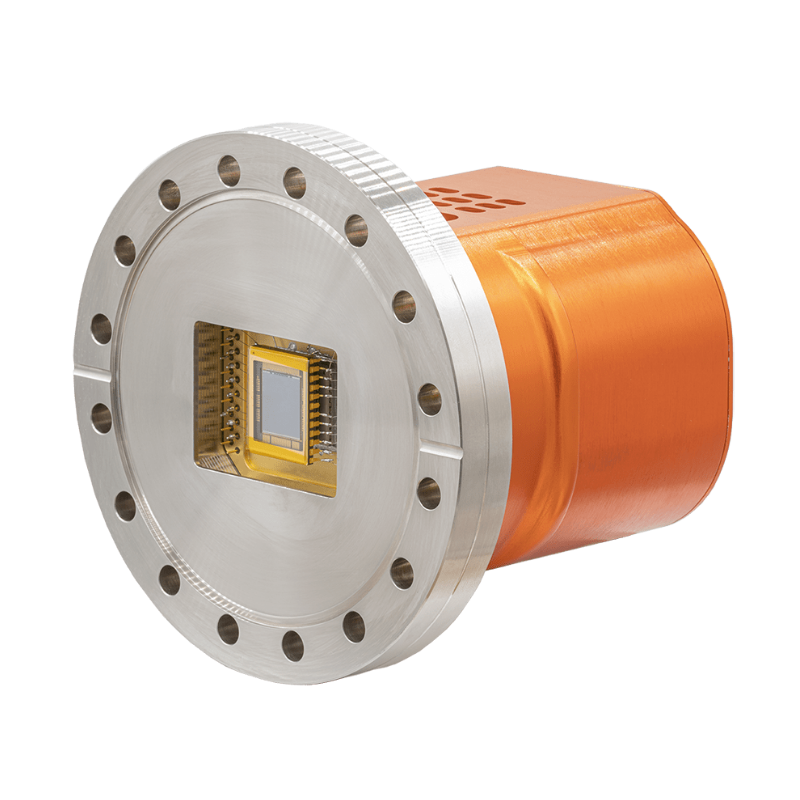
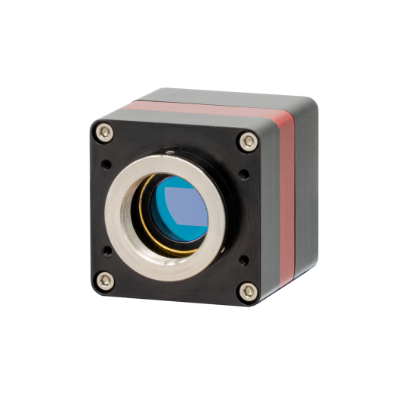
Raptor Photonics is a leading developer and supplier of next generation, high-performance digital camera solutions for the Scientific, Surveillance and Aerospace markets. Raptor offers a range of CCD, EMCCD and lnGaAs solutions.
Specim’s hyperspectral imaging instruments are suited for a whole host of applications including remote sensing, geology, food quality, plastic sorting, online inspection and colour measurement. Additionally, the instruments are extremely versatile, and in most cases the same camera can be configured for use in the lab, field or sky.

Imaging Magazine
Quantum Design UK and Ireland (QDUKI) is proud to bring you this second edition of the popular Imaging Cameras magazine. Packed with case studies, applications, new products and more. Read a free copy of it here…