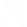Holotomography (HT) technology offers cell biology, bioengineering and biofuel scientists a valuable new tool
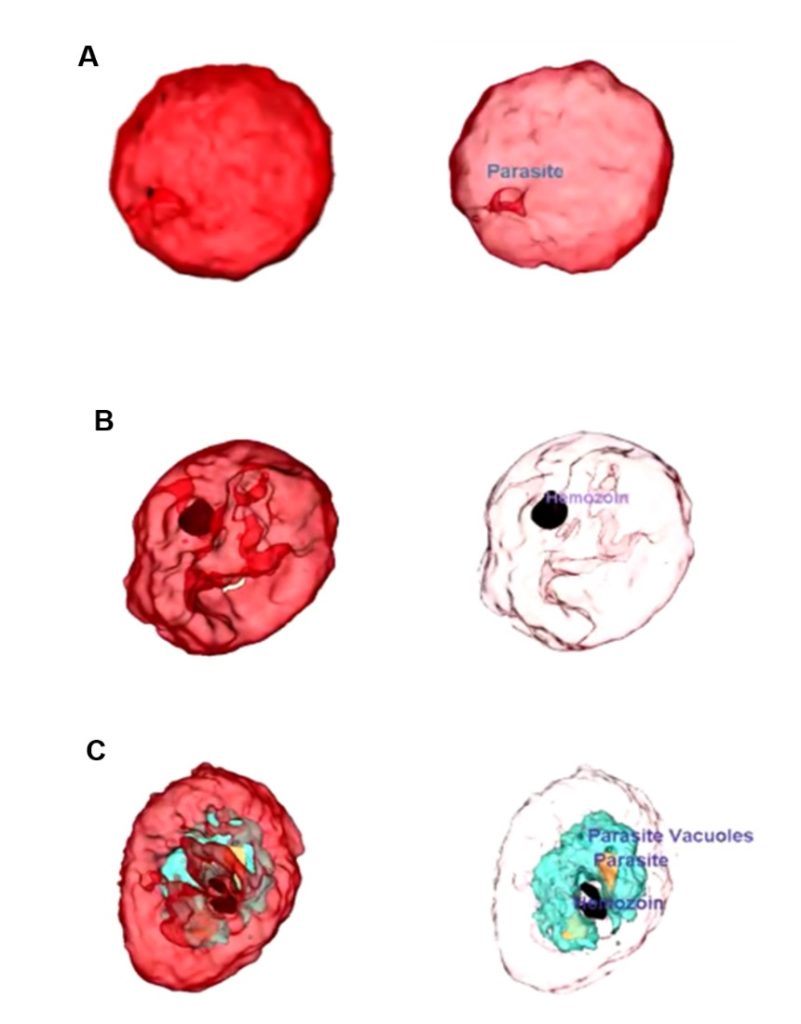
In a breakthrough for research fields as diverse as diabetes, atherosclerosis and biofuels, the mass, concentration, volume, and surface area of individual lipid droplets have been measured in live, unstained cells for the first time using a Tomocube Holotomography (HT) microscope. The elimination of any preparative or staining steps, and the 110nm lateral resolution of the Tomocube HT microscope, means that researchers can now easily track changes in lipid distribution over time in high resolution, enabling metabolic studies of cellular lipid content.
“The immediate quantitative phase images of the intact morphology of live cells is a key advantage of HT microscopy compared to other imaging technologies,” says Aubrey Lambert, Chief Marketing Officer at Tomocube. “Holotomography detects the absolute refractive index (RI) of each voxel by measuring the phase delay. Since the RI of the lipid droplets is distinctly higher than the cytoplasm or other cellular components, the contrast is easily sufficient to image in high resolution.”


Holotomography of a human hepatocyte, Huh-7. 3D tomogram images (Left) fluorescence image (Right). High-RI droplets correlate to the lipid droplets stained by Nile red. 95.5% of organelles whose RI values are higher than n = 1.375 are overlapped to lipid droplets stained by Nile red. Reproduced from Kim et al. Scientific Reports 6:36815
“If the Tomocube HT-2H microscope is used, which supports both holotomography and 3D fluorescence imaging, co-localisation experiments are possible through labelling just the target protein or specific type of fatty acid rather than having to stain both the lipid droplet and the target molecule.”
“Compare this to bright-field or phase contrast microscopy, which conveniently visualises cellular morphology but only provide qualitative information. Confocal fluorescence microscopy does capture high-resolution 3D structural images but involves invasive labelling procedures that inevitably induce phototoxicity or photobleaching.”
For more information on the Tomocube HT microscope visit our Tomocube product page or contact Shayz Ikram on 01372 378822, email shayz@qd-uki.co.uk
References
- Kim K. et al. Three-dimensional label-free imaging and quantification of lipid droplets in live hepatocytes. Scientific Reports (2016) 6:36815.
- Jung J. et al. Label-free non-invasive quantitative measurement of lipid contents in individual microalgal cells using refractive index tomography. Scientific Reports (2018) 8:6524.